This article presents the Trader Edge aggregate neural network model forecast for the March 2016 non-farm payroll data, which is scheduled to be released tomorrow morning at 8:30 AM EDT.
Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) Model Forecast - March 2016
The Trader Edge aggregate NFP model represents the average of three neural network forecasting models, each of which employs a different neural network architecture. Unlike expert systems, neural networks use algorithms to identify and quantify complex relationships between variables based on historical data. All three models derive their forecasts from seven explanatory variables and the changes in those variables over time.
The table in Figure 1 below includes the monthly non-farm payroll data for two months: February and March 2016. The February data was released last month and the non-farm payroll data for March 2016 will be released tomorrow morning at 8:30 AM EDT.
The model forecasts are in the third data row of the table (in blue). Note that past and current forecasts reflect the latest values of the independent variables, which means that forecasts will change when revisions are made to the historical economic data.
The monthly standard error of the model is approximately 81,900 jobs. The first and last data rows of the table report the forecast plus one standard error (in green) and the forecast minus one standard error (in red), respectively. All values are rounded to the nearest thousand. If the model errors were normally distributed, roughly 16% of the observations would fall below minus one standard error and another 16% of the observations would exceed plus one standard error.
The actual non-farm payroll release for February is in the second data row of the table (in purple). The consensus estimate (reported by Briefing.com) for March 2016 is also in the second data row of the table (in purple). The reported and consensus NFP values also include the deviation from the forecast NFP (as a multiple of the standard error of the estimate). Finally, the last column of the table includes the estimated changes from February to March 2016.
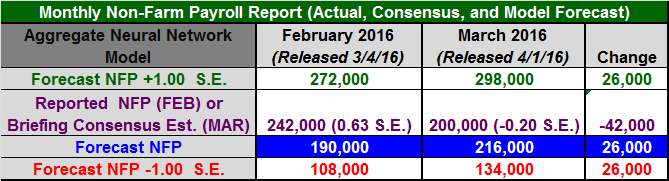
Figure 1: Non-Farm Payroll Table March 2016
Model Commentary
The aggregate neural network model forecast for March is 216,000, which is up 26,000 jobs from last month's revised forecast of 190,000, reflecting a slight strengthening in the employment environment during the month of March. The Briefing.com consensus estimate for March is 200,000, which is 42,000 lower than the February NFP data (242,000), suggesting a material weakening in the employment environment.
The actual February data was significantly above the revised February forecast (+0.63 S.E.) and the consensus estimate for March is slightly below the March model forecast (-0.20 S.E.). The data indicates that the February NFP data was probably inflated, which often results in a modest correction the following month. However, the March forecast is slightly higher than the consensus estimate, which could mitigate the magnitude of the correction in the March data.
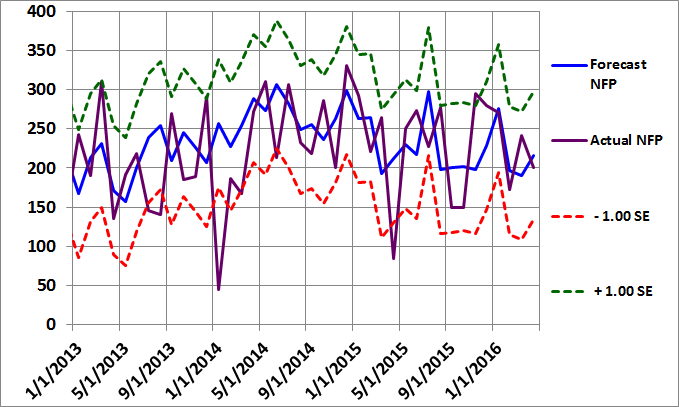
Figure 2: Non-Farm Payroll Graph March 2016
I added a new chart last month (Figure 3 below) to make it easier to observe trends in the employment environment. The blue line depicts the model forecasts (including the latest revisions) and is exactly the same as the Forecast NFP line in Figure 2 above. However, Figure 3 also contains a purple line, which shows the 12-month moving average of the NFP model forecasts.
Why plot the moving average of the model forecasts instead of the actual NFP data? Because the actual NFP data is notoriously noisy. The Forecast NFP data more accurately captures the strength of the employment environment and the stability of the data series makes it easier to observe the trend in employment. This is especially important given the recent increase in recession risk.
We can use the chart below in Figure 3 in two ways to identify the trend in employment. First, we can observe the forecast NFP data relative to the moving average. Observations below the moving average indicate a weakening in employment and vice versa. Second, we can observe the slope of the moving average line. When the moving average line is downward-sloping, employment is weakening and vice versa.
As you can see from the chart in Figure 3, the slope has been negative since early 2015, but may be leveling out. However, the most recent NFP forecast is still below its moving average, which is consistent with the recent data. In fact, 13 of the last 16 forecast observations have been below the moving average line. The employment environment has clearly been weakening for some time and that trend continues. The chart is not shown, but the same trend is evident in the actual NFP data.
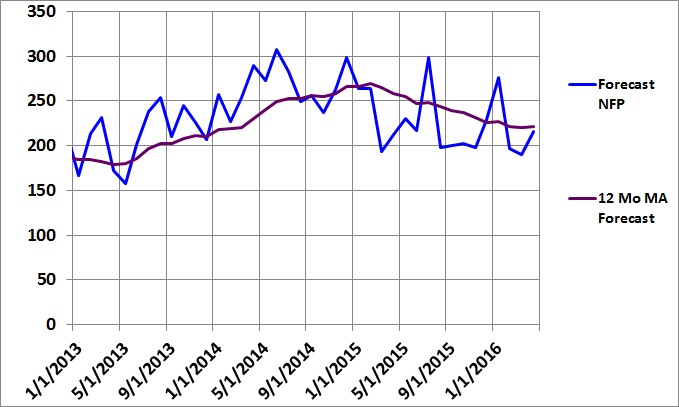
Figure 3: Non-Farm Payroll MA Graph March 2016
Summary
Basic forecasting tools can help you identify unusual consensus economic estimates, which often lead to substantial surprises and market movements. Identifying such environments in advance may help you protect your portfolio from these corrections and help you determine the optimal entry and exit points for your strategies.
In the case of the NFP data, the monthly report data is highly variable and prone to substantial revisions. As a result, having an independent and unbiased indicator of the health of the U.S. job market is especially important.
Print and Kindle Versions of Brian Johnson's 2nd Book are Available on Amazon (75% 5-Star Reviews)
Print and Kindle Versions of Brian Johnson's 1st Book are Available on Amazon (79% 5-Star Reviews)
Trader Edge Strategy E-Subscription Now Available: 20% ROR
The Trader Edge Asset Allocation Rotational (AAR) Strategy is a conservative, long-only, asset allocation strategy that rotates monthly among five large asset classes. The AAR strategy has generated annual returns of approximately 20% over the combined back and forward test period. Please use the above link to learn more about the AAR strategy.
Brian Johnson
Copyright 2016 - Trading Insights, LLC - All Rights Reserved.












