The following article updates the diffusion index, recession slack index, aggregate recession model, and aggregate peak-trough model through October 2014. Please note that two new explanatory variables were added to the Trader Edge Recession Models in July and one explanatory variable was replaced in August. The swapped variables measured similar economic data, but the new series had more predictive power and was more forward-looking. For more information on the two new variables, please see "Two New Improvements to Trader Edge Recession Models."
Diffusion Index
The Trader Edge diffusion index equals the percentage of independent variables indicating a recession. With the recent additions, there are now a total of 18 explanatory variables, each with a unique look-back period and recession threshold. The resulting diffusion index and changes in the diffusion index are used to calculate the probit, logit, and neural network model forecasts.
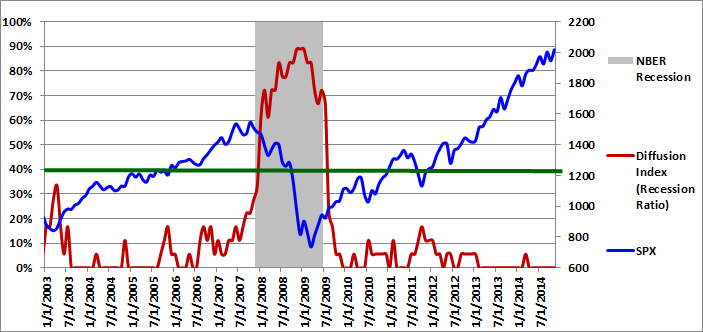
The graph of the diffusion index from 1/1/2003 to 11/1/2014 is presented in Figure 1 below (in red - left axis). If you would like to view a graph of the earlier historical data (going back to 1960), please revisit A New Recession Slack Indicator. The gray shaded regions in Figure 1 below represent U.S. recessions as defined (after the fact) by the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER). The value of the S&P 500 index is also included (in blue - right axis).
In February 2014, for the first time since the end of January 2013, one of the 18 explanatory variables indicated a recession. The number of explanatory variables indicating a recession returned to zero in March and has remained at zero for the past eight months.
Please note that past estimates and index values will change whenever the historical data is revised. All current and past forecasts and index calculations are based on the latest revised data.
Recession Slack Index
The Trader Edge recession slack index equals the median standardized deviation of the current value of the explanatory variables from their respective recession thresholds. The resulting value signifies the amount of slack or cushion relative to the recession threshold, expressed in terms of the number of standard deviations.
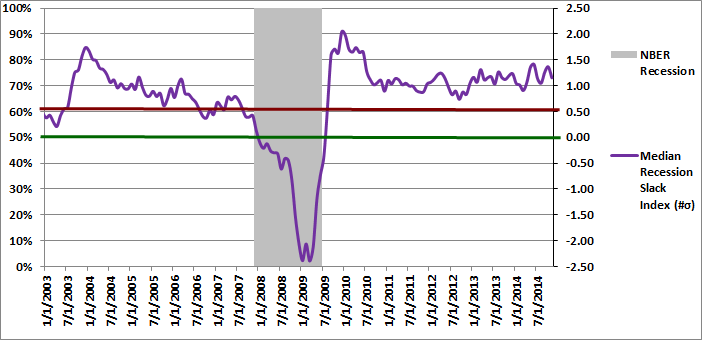
The gray shaded regions in Figure 2 below represent U.S. recessions as defined (after the fact) by the NBER. The median recession slack index is depicted in purple and is plotted against the right axis, which is expressed as the number of standard deviations above the recession threshold.
The dark-red, horizontal line at 0.50 standard deviations denotes a possible warning threshold for the recession slack index. Many of the past recessions began when the recession slack index crossed below 0.50. Similarly, many of the past recessions ended when the recession slack index crossed back above 0.0.
Since emerging from the great recession, 0.74 (on 9/1/2012) was the lowest recorded value of the recession slack index. The recession slack index declined significantly in early 2014 to a low of 0.91 on 3/1/2014, which was the most extreme value recorded since late 2012. Since bottoming out at the end of February, the slack index has fluctuated between a low of 1.07 and a high of 1.41. The slack index declined from 1.37 at the end of September to 1.15 at the end of October, which is still significantly above the warning threshold.
The ability to track small variations and trend changes over time illustrates the advantage of monitoring the continuous recession slack index in addition to the diffusion index above, which moves in discrete steps.
While it is useful to track the actual recession slack index values directly, the values are also used to generate the more intuitive probit and logit probability forecasts.
Aggregate Recession Probability Estimate
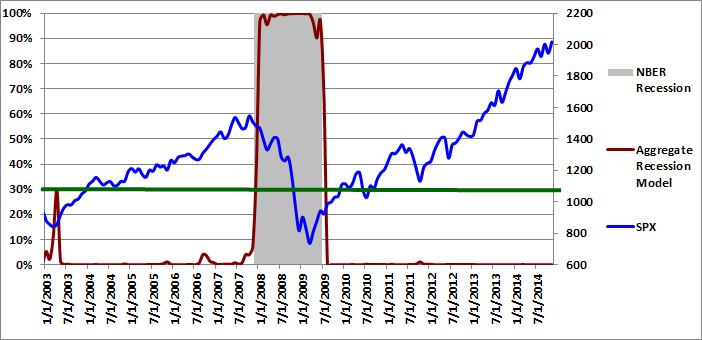
The Trader Edge aggregate recession model is the average of four models: the probit and logit models based on the diffusion index and the probit and logit models based on the recession slack index. The aggregate recession model estimates from 1/1/2003 to 11/1/2014 are depicted in Figure 3 below (red line - left vertical axis). The gray shaded regions represent NBER recessions and the blue line reflects the value of the S&P 500 index (right vertical axis). I suggest using a warning threshold of between 30-40% for the aggregate recession model (green horizontal line).
The aggregate recession model probability estimate for 11/1/2014 was 0.0%, which was unchanged from last month's revised estimate of 0.0%. According to the model, the probability that the U.S. is currently in a recession continues to be extremely remote.
Aggregate Peak-Trough Probability Estimate
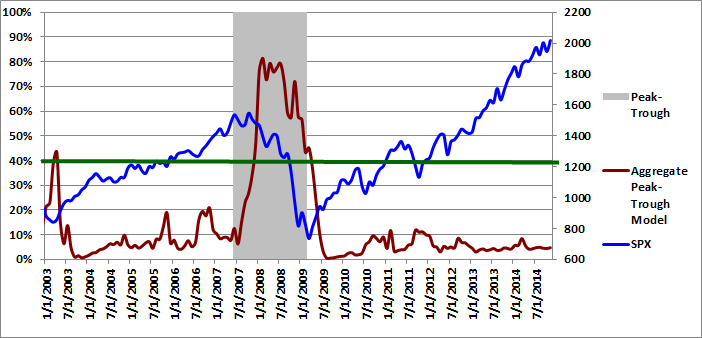
The peak-trough model forecasts are different from the recession model. The peak-trough models estimate the probability of the S&P 500 being between the peak and trough associated with an NBER recession. The S&P 500 typically peaks before recessions begin and bottoms out before recessions end. As a result, it is far more difficult for the peak-trough model to fit this data and the model forecasts have larger errors than the recession model.
The Trader Edge aggregate peak-trough model equals the weighted-average of nine different models: the probit and logit models based on the diffusion index, the probit and logit models based on the recession slack index, and five neural network models.
The aggregate peak-trough model estimates from 1/1/2003 to 11/1/2014 are depicted in Figure 4 below, which uses the same format as Figure 3, except that the shaded regions represent the periods between the peaks and troughs associated with NBER recessions. The aggregate peak-trough model probability estimate for 11/1/2014 was 4.8%, which was up slightly from the revised value of 4.4% at the end of September. The current peak-trough probability estimate of 4.8% is very low and remains significantly below the early warning threshold of 30% to 40%. The highest aggregate peak-trough estimate since the Great Recession was 11.8%, which was recorded on 9/1/2011.
Conclusion
U.S. recession risk remains very low. The diffusion index returned to zero in March and has remained at zero from April through October. The recession slack index has declined slightly from its recent peak of 1.41 at the end of May to 1.15 at the end of October. The peak-trough recession probability estimate decreased from a revised value of 8.5% in February 2014 to 4.8% at the end of October. All of the forecast values are well inside their respective warning thresholds.
Print and Kindle Versions of Brian Johnson's New Book are Now Both Available on Amazon (26 5-Star Reviews)
Trader Edge Strategy E-Subscription Now Available: 20% ROR
The Trader Edge Asset Allocation Rotational (AAR) Strategy is a conservative, long-only, asset allocation strategy that rotates monthly among five large asset classes. The AAR strategy has generated annual returns of approximately 20% over the combined back and forward test period. Please use the above link to learn more about the AAR strategy.
Feedback
Your comments, feedback, and questions are always welcome and appreciated. Please use the comment section at the bottom of this page or send me an email.
Referrals
If you found the information on www.TraderEdge.Net helpful, please pass along the link to your friends and colleagues or share the link with your social or professional networks.
The "Share / Save" button below contains links to all major social and professional networks. If you do not see your network listed, use the down-arrow to access the entire list of networking sites.
Thank you for your support.
Brian Johnson
Copyright 2014 - Trading Insights, LLC - All Rights Reserved.